Back Pain
Regenerative medicine and stem cell therapies hold much promise for the treatment of various injuries and diseases causing pain. Researchers are working on harnessing the process by which stem cells repair and replace damaged tissues and help to decrease the pain
Back pain is a common problem that affects about 80% of people at some point during their life.
The pain may range from a dull aching sensation to severe pain that makes getting out of bed impossible. There are two types of back pain: acute and chronic.
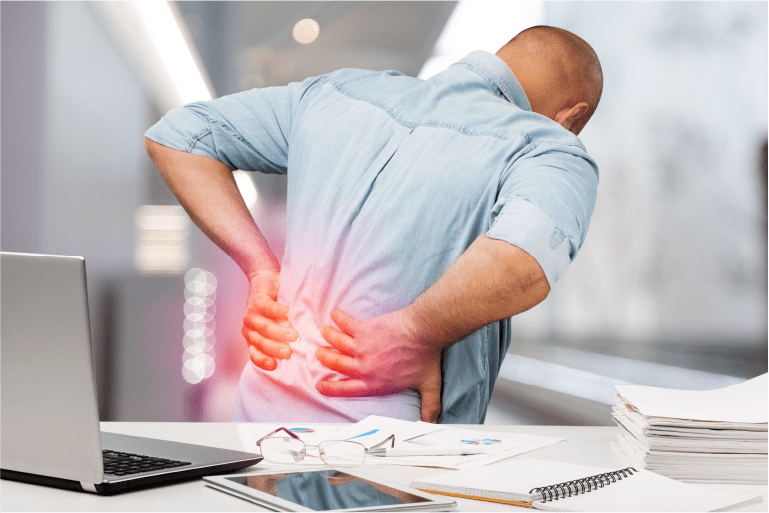
- Acute back pain
- Chronic back pain
Acute back pain is a short-term pain condition resulting from an injury or accident that lasts anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. Most back pain is acute.
Chronic back pain refers to back pain that lasts 12 or more weeks. This type of pain may develop after your acute back pain injury heals or from an underlying degenerative condition. If you suffer from chronic back pain and have tried multiple treatments without getting relief, schedule a consultation with the experts at the International Stem Cell Institute.
Almost half of all back pain causes are related to muscle contusion and strain. Muscle tissue is comprised of long, tubular cells called myoblasts, which fuse to form muscle fibers. Muscle stem cells, also known as satellite cells are responsible for muscle repair. During exercise, muscle fibers become damaged and send signals to satellite cells that sit on top of the muscle tissue. In response to these signals the satellite cells become activated, begin to divide, and as well as making copies of themselves, generate new myoblast cells. These myoblasts are then integrated and repair the damaged muscle tissue.
UCMSCs are adult stem cells which, as well as being able to produce copies of themselves, can divide and form bone, cartilage, muscle, and adipose cells when cultured in the appropriate conditions. MSCs produce proteins that are suggested to alter the surrounding environment and promote healing and tissue regeneration, such as anti-inflammatory factors, angiogenic factors (which promote the growth of new blood vessels) and other factors, which stimulate local, tissue-specific stem cells.
Most back pain develops from a mechanical problem that affects the structure and function of your back and spine. Common causes include:
- Sprains and strains.
- Herniated or bulging discs.
- Arthritis.
- Degenerative disc disease.
- Spinal nerve compression.
- Sciatica.
- Spinal stenosis.
- Vertebral compression fractures.
Stem cells are being investigated in each of these areas. Some investigations are determining if stem cells speed healing and recovery. Stem cells are typically deployed by injection into the affected area(s) and intravenously (IV). Early investigations suggest that using both local injections and IV deployment enhances the outcomes. Most of the injection sites such as most soft tissue and joints can be done directly at Innovations Medical. Some such as injections in the back or neck require special imaging and are done at a separate location where radiologic imaging like CT scan is available. Typically all of these injections and the IV are done under local anesthesia without the need for sedation.
Contrary to other Stem Cell treatments based on autologous transplant, where the stem cells are as old as the patient’s age and carry all the information accumulated through their life, at International Stem Cell Institute®, we use donor umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) instead of bone marrow or fat tissue-derived. In our laboratory, umbilical cord MSCs can undergo approximately twice the number of “doublings” as their adult-derived bone marrow or fat tissue counterparts. The overall hypothesis is that UCMS cells possess immune properties that would be permissive to allogeneic transplantation. For example, UCMS cells will suppress the proliferation of “stimulated” lymphocytes (immune suppression) and have reduced immunogenicity (e.g., would be poor stimulators of allogeneic lymphocyte proliferation).
Mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors for several connective tissue cell lineages, including bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, and bone marrow. As mesenchymal stem cells can target diseased organs, they may hold potential as vehicles capable of expressing and secreting proteins with therapeutic effects. These conditions are ailments and disorders in muscles, ligaments, and joints. Common examples include Rheumatoid Arthritis, degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, and various injuries like fractures and torn cartilage.
International Stem Cell Institute® Stem Cell Procedures
Help overcome these conditions by extracting stem cells from the umbilical cord, then concentrating and culture the cells and injecting them into the damaged area to help the body heal naturally. Our Stem Cell Procedures can be used for a wide range of conditions and are the tool of choice for injuries, arthritis, and other conditions that may be more significant than those treated with conventional therapies. According to our research, stem cells have self-renewal qualities which aid in reproducing cartilage and bone tissue cells, restoring joint function, and reducing pain. Scientists have discovered that stem cells and specifically allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, are home to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents. Usually, these cells are harvested from human umbilical cords donated after normal healthy births. This means that stem cell transplants could be used to treat some of the most common osteoarticular symptoms.
- Everything about your International Stem Cell Institute® experience is designed for results.
- At the International Stem Cell Institute®, our priority is to produce the best possible outcomes for our patients.
- And while our protocol is far more complex than you will find at other regenerative medicine clinics, we do not cut corners.
The injection typically takes place three weeks after the UCMSCs are extracted from the umbilical cord. During this time, cells are grown for approximately 15 days and then tested for quality assurance, including sterility testing and karyotype analysis to ensure no genetic abnormalities present in the stem cells. Once the UCMSCs have passed all safety and quality testing, you will be scheduled for the injection procedure. During the injection, the cultured cells are thoroughly tested for quality assurance and injected using guided imaging to ensure the most precise placement of cells into the injured area.
Neck Pain
Regenerative medicine and stem cell therapies hold much promise for the treatment of various injuries and diseases causing pain. Researchers are working on harnessing the process by which stem cells repair and replace damaged tissues and help to decrease the pain.
While a relatively small area of your body, your neck is a complex structure that performs numerous functions.
Not only does your neck house and protect your spinal cord, esophagus, trachea, and thyroid gland, it also plays a critical role in head movement.
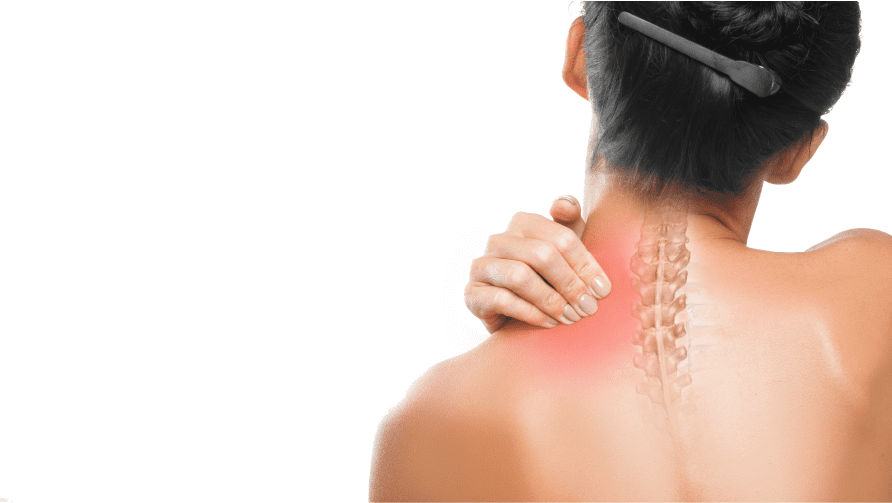
The neck also houses your cervical spine, including the uppermost vertebrae, connective tissues, nerves, and blood vessels. A problem with any of these joint components can lead to serious neck pain.
-
Traumatic injury.
-
Sports injuries.
-
Muscle strain.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Nerve compression.
-
Joint degeneration.
-
Whiplash.
-
Poor posture.
- There is no clear cause
- Stem cells are typically injected
- If you suffer from neck pain
Contrary to other Stem Cell treatments based on autologous transplant, where the stem cells are as old as the patient’s age and carry all the information accumulated through their life, at the International Stem Cell Institute®, we use donor umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) instead of bone marrow or fat tissue-derived. In our laboratory, umbilical cord MSCs can undergo approximately twice the number of “doublings” as their adult-derived bone marrow or fat tissue counterparts. The overall hypothesis is that UCMS cells possess immune properties that would be permissive to allogeneic transplantation. For example, UCMS cells will suppress the proliferation of “stimulated” lymphocytes (immune suppression) and have reduced immunogenicity (e.g., would be poor stimulators of allogeneic lymphocyte proliferation).
Mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors for several connective tissue cell lineages, including bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, and bone marrow. As mesenchymal stem cells can target diseased organs, they may hold potential as vehicles capable of expressing and secreting proteins with therapeutic effects. These conditions are ailments and disorders in muscles, ligaments, and joints. Common examples include Rheumatoid Arthritis, degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, and various injuries like fractures and torn cartilage.
International Stem Cell Institute® Stem Cell Procedures
Help overcome these conditions by extracting stem cells from the umbilical cord, then concentrating and culture the cells and injecting them into the damaged area to help the body heal naturally. Our Stem Cell Procedures can be used for a wide range of conditions and are the tool of choice for injuries, arthritis, and other conditions that may be more significant than those treated with conventional therapies. According to our research, stem cells have self-renewal qualities which aid in reproducing cartilage and bone tissue cells, restoring joint function, and reducing pain. Scientists have discovered that stem cells and specifically allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, are home to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents. Usually, these cells are harvested from human umbilical cords donated after normal healthy births. This means that stem cell transplants could be used to treat some of the most common osteoarticular symptoms.
- Everything about your International Stem Cell Institute® experience is designed for results.
- At the International Stem Cell Institute®, our priority is to produce the best possible outcomes for our patients.
- And while our protocol is far more complex than you will find at other regenerative medicine clinics, we do not cut corners.
The injection typically takes place three weeks after the UCMSCs are extracted from the umbilical cord. During this time, cells are grown for approximately 15 days and then tested for quality assurance, including sterility testing and karyotype analysis to ensure no genetic abnormalities present in the stem cells. Once the UCMSCs have passed all safety and quality testing, you will be scheduled for the injection procedure. During the injection, the cultured cells are thoroughly tested for quality assurance and injected using guided imaging to ensure the most precise placement of cells into the injured area.
Stop just managing symptoms
get to the root cause
Shoulder Pain
Regenerative medicine and stem cell therapies hold much promise for the treatment of various injuries and diseases causing pain. Researchers are working on harnessing the process by which stem cells repair and replace damaged tissues and help to decrease the pain.
The shoulder is the most movable joint in the human body.
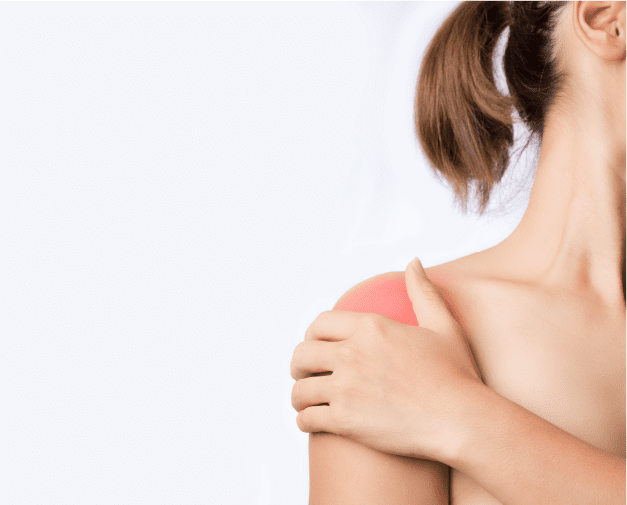

A group of four muscles and their tendons, called the rotator cuff, give the shoulder its wide range of motion. Swelling, damage, or bone changes around the rotator cuff can cause shoulder pain. The most common cause of shoulder pain occurs when rotator cuff tendons become trapped under the bony area in the shoulder. The tendons become inflamed or damaged. This condition is called rotator cuff tendinitis or bursitis.
Shoulder pain may also be caused by:
-
Arthritis in the shoulder joint.
-
Bone spurs in the shoulder area.
-
Bursitis, which is inflammation of a fluid-filled sac (bursa) that normally protects the joint and helps it move smoothly.
-
Broken shoulder bone.
-
Dislocation of the shoulder.
-
Shoulder separation.
-
Frozen shoulder, which occurs when the muscles, tendons, and ligaments inside the shoulder become stiff, making movement difficult and painful.
-
Overuse or injury of nearby tendons, such as the bicep muscles of the arms.
-
Nerve injury that leads to abnormal shoulder movement.
-
Tears of the rotator cuff tendons.
-
Poor shoulder posture and mechanics.
Sometimes, shoulder pain may be due to a problem in another area of the body, such as the neck or lungs. This is called referred pain. There is usually pain at rest and no worsening of pain when moving the shoulder.
- ¿Stem cells speed healing and recovery?
- If you suffer from shoulder pain
Contrary to other Stem Cell treatments based on autologous transplant, where the stem cells are as old as the patient’s age and carry all the information accumulated through their life, at the International Stem Cell Institute®, we use donor umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) instead of bone marrow or fat tissue-derived. In our laboratory, umbilical cord MSCs can undergo approximately twice the number of “doublings” as their adult-derived bone marrow or fat tissue counterparts. The overall hypothesis is that UCMS cells possess immune properties that would be permissive to allogeneic transplantation. For example, UCMS cells will suppress the proliferation of “stimulated” lymphocytes (immune suppression) and have reduced immunogenicity (e.g., would be poor stimulators of allogeneic lymphocyte proliferation).
Mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors for several connective tissue cell lineages, including bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, and bone marrow. As mesenchymal stem cells can target diseased organs, they may hold potential as vehicles capable of expressing and secreting proteins with therapeutic effects. These conditions are ailments and disorders in muscles, ligaments, and joints. Common examples include Rheumatoid Arthritis, degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, and various injuries like fractures and torn cartilage.
International Stem Cell Institute® Stem Cell Procedures
Help overcome these conditions by extracting stem cells from the umbilical cord, then concentrating and culture the cells and injecting them into the damaged area to help the body heal naturally. Our Stem Cell Procedures can be used for a wide range of conditions and are the tool of choice for injuries, arthritis, and other conditions that may be more significant than those treated with conventional therapies. According to our research, stem cells have self-renewal qualities which aid in reproducing cartilage and bone tissue cells, restoring joint function, and reducing pain. Scientists have discovered that stem cells and specifically allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, are home to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents. Usually, these cells are harvested from human umbilical cords donated after normal healthy births. This means that stem cell transplants could be used to treat some of the most common osteoarticular symptoms.
- Everything about your International Stem Cell Institute® experience is designed for results.
- At the International Stem Cell Institute®, our priority is to produce the best possible outcomes for our patients.
- And while our protocol is far more complex than you will find at other regenerative medicine clinics, we do not cut corners.
The injection typically takes place three weeks after the UCMSCs are extracted from the umbilical cord. During this time, cells are grown for approximately 15 days and then tested for quality assurance, including sterility testing and karyotype analysis to ensure no genetic abnormalities present in the stem cells. Once the UCMSCs have passed all safety and quality testing, you will be scheduled for the injection procedure. During the injection, the cultured cells are thoroughly tested for quality assurance and injected using guided imaging to ensure the most precise placement of cells into the injured area.
Sciatica
Regenerative medicine and stem cell therapies hold much promise for the treatment of various injuries and diseases causing pain. Researchers are working on harnessing the process by which stem cells repair and replace damaged tissues and help to decrease the pain. Sciatica is a form of pain that originates in your sciatic nerve, the longest single nerve in your body. Your sciatic nerve begins in your lower back and extends downward through your buttocks and into each leg.
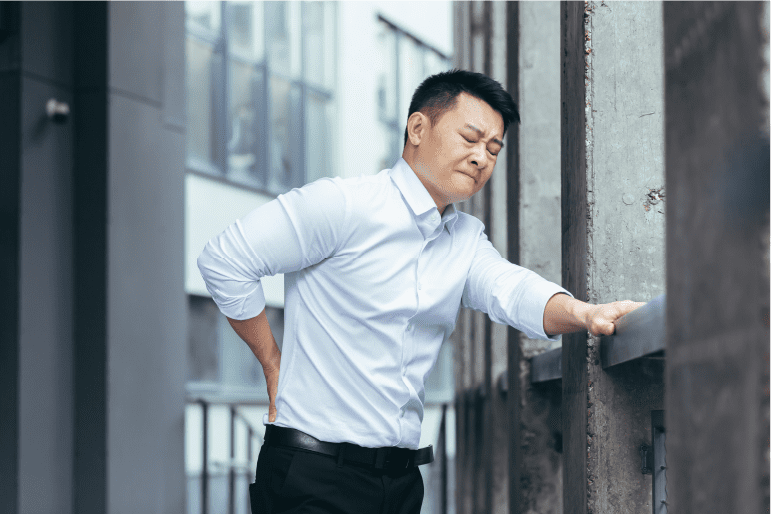

Like all nerve tissues, when your sciatic nerve is placed under undue pressure it sends pain signals to your brain. A common cause of sciatica is a herniated disc in your lower spine. When one of the firm, rubbery discs that cushion your vertebra becomes worn down the softer central tissue can begin to bulge out and press against your sciatic nerve. Unlike many types of pain, sciatica is relatively easy to diagnose. Sciatica creates pain that begins in your lower back and radiates down into the back or side of one leg. That pain can be a sharp, burning sensation or a dull throbbing discomfort.
Additional symptoms of sciatica include:
-
Pain that worsens after prolonged periods of sitting.
-
Pain that flares up when you cough or sneeze.
-
Sensations of numbness or weakness in your leg or foot.
-
Difficulty moving your leg or foot.
Sciatica pain almost always occurs only on one side of your body. It can range from mild to severe and can be steady or intermittent. Stem cells are being investigated in each of these areas. Some investigations are determining if stem cells speed healing and recovery.
- Stem cells are typically injected
- If you suffer from sciatica
Contrary to other Stem Cell treatments based on autologous transplant, where the stem cells are as old as the patient’s age and carry all the information accumulated through their life, at the International Stem Cell Institute®, we use donor umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) instead of bone marrow or fat tissue-derived. In our laboratory, umbilical cord MSCs can undergo approximately twice the number of “doublings” as their adult-derived bone marrow or fat tissue counterparts. The overall hypothesis is that UCMS cells possess immune properties that would be permissive to allogeneic transplantation. For example, UCMS cells will suppress the proliferation of “stimulated” lymphocytes (immune suppression) and have reduced immunogenicity (e.g., would be poor stimulators of allogeneic lymphocyte proliferation).
Mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors for several connective tissue cell lineages, including bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, and bone marrow. As mesenchymal stem cells can target diseased organs, they may hold potential as vehicles capable of expressing and secreting proteins with therapeutic effects. These conditions are ailments and disorders in muscles, ligaments, and joints. Common examples include Rheumatoid Arthritis, degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, and various injuries like fractures and torn cartilage.
International Stem Cell Institute® Stem Cell Procedures
Help overcome these conditions by extracting stem cells from the umbilical cord, then concentrating and culture the cells and injecting them into the damaged area to help the body heal naturally. Our Stem Cell Procedures can be used for a wide range of conditions and are the tool of choice for injuries, arthritis, and other conditions that may be more significant than those treated with conventional therapies. According to our research, stem cells have self-renewal qualities which aid in reproducing cartilage and bone tissue cells, restoring joint function, and reducing pain. Scientists have discovered that stem cells and specifically allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, are home to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents. Usually, these cells are harvested from human umbilical cords donated after normal healthy births. This means that stem cell transplants could be used to treat some of the most common osteoarticular symptoms.
- Everything about your International Stem Cell Institute® experience is designed for results.
- At the International Stem Cell Institute® our priority is to produce the best possible outcomes for our patients.
- And while our protocol is far more complex than you will find at other regenerative medicine clinics, we do not cut corners.
The injection typically takes place three weeks after the UCMSCs are extracted from the umbilical cord. During this time, cells are grown for approximately 15 days and then tested for quality assurance, including sterility testing and karyotype analysis to ensure no genetic abnormalities present in the stem cells. Once the UCMSCs have passed all safety and quality testing, you will be scheduled for the injection procedure. During the injection, the cultured cells are thoroughly tested for quality assurance and injected using guided imaging to ensure the most precise placement of cells into the injured area.
Ignite Your Journey to
Pain-Free Living Now!
Osteoarthritis
Sometimes called degenerative joint disease or degenerative arthritis, osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common chronic condition of the joints, affecting approximately 27 million Americans. OA can affect any joint, but it occurs most often in knees, hips, lower back and neck, small joints of the fingers and the bases of the thumb and big toe.
In OA, the cartilage breaks down, causing pain, swelling and problems moving the joint. As OA worsens over time, bones may break down and develop growths called spurs. Bits of bone or cartilage may chip off and float around in the joint.
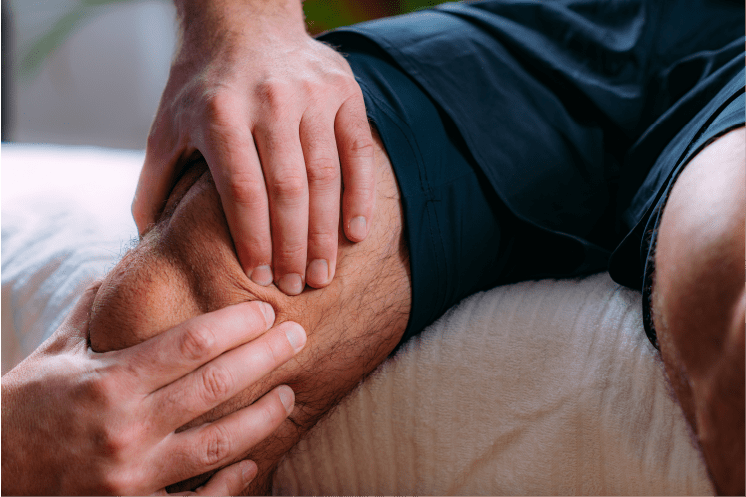
In the body, an inflammatory process occurs and cytokines (proteins) and enzymes develop that further damage the cartilage. In the final stages of OA, the cartilage wears away and bone rubs against bone leading to joint damage and more pain.
- The stem cell therapy, designed to target these areas within the joints
- UCMSCs can easily expand
The stem cell therapy used at the International Stem Cell Institute® is designed to target these areas within the joints to help with the creation of new cartilage cells. As mesenchymal stem cells are multipotent they have the ability to differentiate into cartilage called (chondrocytes). The goal of each stem cell treatment is to inject the stem cells into the joint to create cartilage (chondrocyte cells). Stem cells are also a natural anti inflammatory, which can assist with osteoarthritis pain and swelling in the joint area. These procedures may help patients who don’t respond to typical drug treatment, want to reduce their reliance on medication or are looking to try stem cell therapy before starting drug treatment
Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UCMSCs), which have the ability to differentiate into cells of the chondrogenic lineage, have emerged as a candidate cell type with great potential for cell-based articular cartilage repair technologies. UCMSCs can readily culture-expanded without losing their multi lineage differentiation potential, and have been induced to undergo chondrogenic differentiation in vitro and in vivo. Unlike chondrocytes, the use of MSCs is not hindered by the limited availability of healthy articular cartilage or an intrinsic tendency of the cells to lose their phenotype during expansion. The use of MSCs also obviates the need for a cartilage biopsy and, thereby, avoids morbidity caused by damage to the donor-site articular surface.
Contrary to other Stem Cell treatments based on autologous transplant, where the stem cells are as old as the patient’s age and carry all the information accumulated through their life, at the International Stem Cell Institute®, we use donor umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) instead of bone marrow or fat tissue-derived. In our laboratory, umbilical cord MSCs can undergo approximately twice the number of “doublings” as their adult-derived bone marrow or fat tissue counterparts. The overall hypothesis is that UCMS cells possess immune properties that would be permissive to allogeneic transplantation. For example, UCMS cells will suppress the proliferation of “stimulated” lymphocytes (immune suppression) and have reduced immunogenicity (e.g., would be poor stimulators of allogeneic lymphocyte proliferation).
Mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors for several connective tissue cell lineages, including bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, and bone marrow. As mesenchymal stem cells can target diseased organs, they may hold potential as vehicles capable of expressing and secreting proteins with therapeutic effects. These conditions are ailments and disorders in muscles, ligaments, and joints. Common examples include Rheumatoid Arthritis, degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, and various injuries like fractures and torn cartilage.
International Stem Cell Institute® Stem Cell Procedures
Help overcome these conditions by extracting stem cells from the umbilical cord, then concentrating and culture the cells and injecting them into the damaged area to help the body heal naturally. Our Stem Cell Procedures can be used for a wide range of conditions and are the tool of choice for injuries, arthritis, and other conditions that may be more significant than those treated with conventional therapies. According to our research, stem cells have self-renewal qualities which aid in reproducing cartilage and bone tissue cells, restoring joint function, and reducing pain. Scientists have discovered that stem cells and specifically allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, are home to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents. Usually, these cells are harvested from human umbilical cords donated after normal healthy births. This means that stem cell transplants could be used to treat some of the most common osteoarticular symptoms.
- Everything about your International Stem Cell Institute® experience is designed for results.
- At the International Stem Cell Institute®, our priority is to produce the best possible outcomes for our patients.
- And while our protocol is far more complex than you will find at other regenerative medicine clinics, we do not cut corners.
The injection typically takes place three weeks after the UCMSCs are extracted from the umbilical cord. During this time, cells are grown for approximately 15 days and then tested for quality assurance, including sterility testing and karyotype analysis to ensure no genetic abnormalities present in the stem cells. Once the UCMSCs have passed all safety and quality testing, you will be scheduled for the injection procedure. During the injection, the cultured cells are thoroughly tested for quality assurance and injected using guided imaging to ensure the most precise placement of cells into the injured area.
Sports Injuries
Regenerative medicine and stem cell therapies hold much promise for the treatment of various injuries and diseases suffered by sportspeople. Researchers are working on harnessing the process by which stem cells repair and replace damaged tissues and cells.
Almost half of all sports-related injuries are related to muscle contusion and strain. Muscle tissue is comprised of long, tubular cells called myoblasts, which fuse to form muscle fibers. Muscle stem cells, also known as satellite cells are responsible for muscle repair.
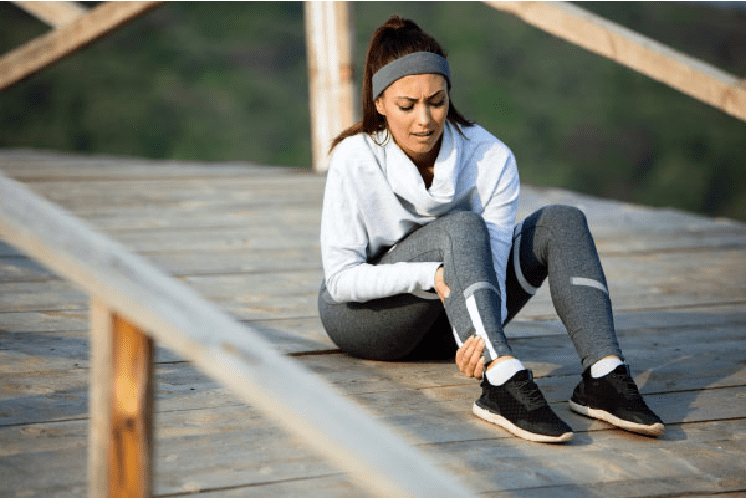

During exercise, muscle fibers become damaged and send signals to satellite cells that sit on top of the muscle tissue. In response to these signals the satellite cells become activated, begin to divide, and as well as making copies of themselves, generate new myoblast cells. These myoblasts are then integrated and repair the damaged muscle tissue.
- There are many types of sports injuries.
- Stem cells are typically injected
UCMSCs are adult stem cells which, as well as being able to produce copies of themselves, can divide and form bone, cartilage, muscle, and adipose cells when cultured in the appropriate conditions. MSCs produce proteins that are suggested to alter the surrounding environment and promote healing and tissue regeneration, such as anti-inflammatory factors, angiogenic factors (which promote the growth of new blood vessels) and other factors, which stimulate local, tissue-specific stem cells.
There are many types of sports injuries. Sports injuries can involve almost any area of the body. We can group most sports injuries into five categories:
- Bone injuries – including brakes or fracture and “bruising”.
- Soft tissue injuries – including muscle, ligaments, tendons, cartilage and skin scrapes and bruises.
- Joint injuries – including dislocations, separations and post-injury arthritis.
- Head injuries – primarily concussions.
- Overuse injuries – usually involve soft tissue or joints but caused by repetitive activities.
Stem cells are being investigated in each of these areas. Some investigations are determining if stem cells speed healing and recovery.
Stem cells are typically deployed by injection into the affected area(s) and intravenously (IV). Early investigations suggest that using both local injections and IV deployment enhances the outcomes. Most of the injection sites such as most soft tissue and joints can be done directly at Innovations Medical. Some such as injections in the back or neck require special imaging and are done at a separate location where radiologic imaging like CT scan is available. Typically all of these injections and the IV are done under local anesthesia without the need for sedation.
Contrary to other Stem Cell treatments based on autologous transplant, where the stem cells are as old as the patient’s age and carry all the information accumulated through their life, at the International Stem Cell Institute®, we use donor umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) instead of bone marrow or fat tissue-derived. In our laboratory, umbilical cord MSCs can undergo approximately twice the number of “doublings” as their adult-derived bone marrow or fat tissue counterparts. The overall hypothesis is that UCMS cells possess immune properties that would be permissive to allogeneic transplantation. For example, UCMS cells will suppress the proliferation of “stimulated” lymphocytes (immune suppression) and have reduced immunogenicity (e.g., would be poor stimulators of allogeneic lymphocyte proliferation).
Mesenchymal stem cells are progenitors for several connective tissue cell lineages, including bone, cartilage, muscle, fat, and bone marrow. As mesenchymal stem cells can target diseased organs, they may hold potential as vehicles capable of expressing and secreting proteins with therapeutic effects. These conditions are ailments and disorders in muscles, ligaments, and joints. Common examples include Rheumatoid Arthritis, degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, and various injuries like fractures and torn cartilage.
International Stem Cell Institute® Stem Cell Procedures
Help overcome these conditions by extracting stem cells from the umbilical cord, then concentrating and culture the cells and injecting them into the damaged area to help the body heal naturally. Our Stem Cell Procedures can be used for a wide range of conditions and are the tool of choice for injuries, arthritis, and other conditions that may be more significant than those treated with conventional therapies. According to our research, stem cells have self-renewal qualities which aid in reproducing cartilage and bone tissue cells, restoring joint function, and reducing pain. Scientists have discovered that stem cells and specifically allogeneic umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, are home to inflamed tissue and start producing anti-inflammatory agents. Usually, these cells are harvested from human umbilical cords donated after normal healthy births. This means that stem cell transplants could be used to treat some of the most common osteoarticular symptoms.
- Everything about your International Stem Cell Institute® experience is designed for results.
- At the International Stem Cell Institute®, our priority is to produce the best possible outcomes for our patients.
- And while our protocol is far more complex than you will find at other regenerative medicine clinics, we do not cut corners.
The injection typically takes place three weeks after the UCMSCs are extracted from the umbilical cord. During this time, cells are grown for approximately 15 days and then tested for quality assurance, including sterility testing and karyotype analysis to ensure no genetic abnormalities present in the stem cells. Once the UCMSCs have passed all safety and quality testing, you will be scheduled for the injection procedure. During the injection, the cultured cells are thoroughly tested for quality assurance and injected using guided imaging to ensure the most precise placement of cells into the injured area.
Orthopedic Degenerative Conditions
In the landscape of regenerative medicine, Dr. Leonardo Gonzalez stands as a visionary, particularly in treating orthopedic degenerative conditions. These conditions, which affect millions of Americans, are characterized by the deterioration of cartilage, bone, and tissues, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility.

Orthopedic degenerative diseases encompass a range of conditions, such as osteoarthritis, which affects over 32.5 million U.S. adults, and degenerative disc disease, prevalent in approximately 40% of people aged 40 and rising to 80% in those aged 80. These statistics not only highlight the scale of the issue but also underscore the urgent need for effective treatments.
The Role of MSCWJ in Orthopedic Regeneration
Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Wharton’s Jelly (MSCWJ) have emerged as a revolutionary force in this field. Their unique properties make them ideally suited for addressing orthopedic degenerative conditions:
- Regenerative Capability
- Anti-inflammatory Properties
- Immunomodulatory Effects
MSCWJ can differentiate into bone, cartilage, and muscle cells, making them perfect for repairing and regenerating damaged orthopedic tissues.
They can reduce inflammation, a key contributor to pain and progression in degenerative conditions.
MSCWJ can modulate the immune system, preventing abnormal immune responses that can exacerbate orthopedic conditions.
Dr. Leonardo Gonzalez’s Unique Approach
What sets Dr. Leonardo Gonzalez apart is his innovative use of image-guided delivery techniques for MSCWJ. Unlike traditional approaches, Dr. Gonzalez employs:
· CT-Guided Injections: Offering precise delivery to the exact location of tissue degeneration.
· Fluoroscopy: Ensuring real-time visualization and accuracy in stem cell deployment.
· Cath Lab Procedures: For targeted intravascular delivery, reaching deeper tissues.
· IV Infusion: Utilized when systemic treatment is necessary, spreading regenerative potential throughout the body.
These advanced techniques ensure that MSCWJ is delivered precisely where it’s needed most, enhancing efficacy and outcomes for patients with orthopedic degenerative conditions.
Dr. Gonzalez’s Clinic in Bogota, Colombia
Due to regulatory constraints in the USA, Dr. Gonzalez operates from Bogota, Colombia. This location allows him to provide advanced and unrestricted stem cell treatments, focusing on treating the cause, not just the symptoms, of orthopedic degenerative diseases.
The Impact and Future Outlook
Patients treated with MSCWJ under Dr. Gonzalez’s care have reported significant improvements in pain, mobility, and quality of life. These advancements signal a paradigm shift in treating orthopedic degenerative conditions, moving away from symptom management to actual healing and regeneration.
2023 © Mercadeo Salud. All rights reserved.

